SEO for Business Owners
Summary
SEO helps your website appear higher in Google search results so more people can find your business. It starts with using clear titles, relevant keywords, and well-structured headings. Optimise your meta title, description, and URLs, and make sure your content is easy to read and mobile-friendly. Don’t forget to compress images and add keyword-rich alt text. Internal and external links boost credibility, and calls to action help turn visitors into customers. Use tools like SEOPress and Google Search Console to track performance and make improvements. Done right, SEO brings in more traffic, more leads, and better results over time.
Use tools like SEOPress to analyse and improve your on-page SEO
Review your performance in Google Search Console after publishing
SEO (Search Engine Optimisation) helps your pages and blog posts rank higher on search engines, making them more visible to potential visitors.
A well-optimised page ensures your website gets targeted traffic and better engagement.
How Search Engines Determine Relevance
Search engines, and now AI search assistants, don’t just match keywords anymore. They evaluate how clearly your website demonstrates expertise, trust, and real-world relevance.
Here’s what matters most in 2026:
- Topical and semantic relevance – Your content needs to fully answer the intent behind a search, not just repeat the keywords. Google’s AI Overviews and generative results now prioritise clear, structured, and fact-supported information.
- Content depth and clarity – Pages that demonstrate first-hand expertise (E-E-A-T: Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) perform better across both traditional search and AI citations.
- User experience & Core Web Vitals – Fast-loading, mobile-optimised, and visually stable pages rank higher. Google rewards websites that people actually stay on and interact with.
- Entity authority & backlinks – Consistent brand mentions, citations, and links from reputable or locally relevant sources strengthen your digital “trust graph.”
- AI-readable structure – Clean HTML, strong headings, schema markup, and clear internal linking make it easier for AI models (like Google Gemini and ChatGPT) to understand, quote, and recommend your content.
Readability & “Answer-First” Structure
To win in 2026 and beyond, content must be machine-readable and modular.
Creating Citation-Worthy Content
- The “Answer-First” Model: Provide a concise, direct answer (40–60 words) to the main question in the first two paragraphs of the page.
- Modular Formatting: Use clear H2 and H3 headers framed as the questions your customers actually ask. Treat each section as a “standalone” lesson that an AI can easily extract.
- Micro-Paragraphs: Keep paragraphs to 2–4 sentences. Large “walls of text” are difficult for both mobile users to read and AI models to parse accurately.
- Use Proof Markers: Include specific numbers, case study references, and “last updated” dates. AI prioritizes verifiable facts over generic advice.
Find your Voice Gap
If one business owner writes a blog post about “5 Tips for Lawn Care” that looks exactly like the other 5 million posts on the web, AI will just summarize the topic and never cite their website. “What do you say that your competitors are afraid to say or haven’t thought to mention?” or “What is a common myth in your industry you can debunk?” Unique perspectives are “citation gold” for AI.
Helpful tools for helpful content
Google prioritises content that answers user intent clearly and concisely. Use Grammarly’s Readability Score or Hemingway Editor’s readability checker to calculate the average level of education needed to understand your content.
Site Structure, Slugs and Permalinks
A clean, descriptive URL helps both search engines and users understand your content instantly, and it’s still one of the strongest on-page ranking signals. Once your site is live, avoid changing established URLs unless necessary, update with 301 redirects to keep your SEO equity intact.
Best Practices for URLs
- Keep them short, descriptive, and human-readable.
- Include your main keyword or topic phrase naturally, avoid repetition.
- Use hyphens (-) between words, never underscores or symbols.
- Avoid dynamic URLs (e.g. with
?id=123) unless required for technical reasons. - Stick to lowercase. Mixed case URLs can cause duplication issues.
Good: yourwebsite.com/ballarat-web-design/
Not Like this: yourwebsite.com/blog-post-12345/ (
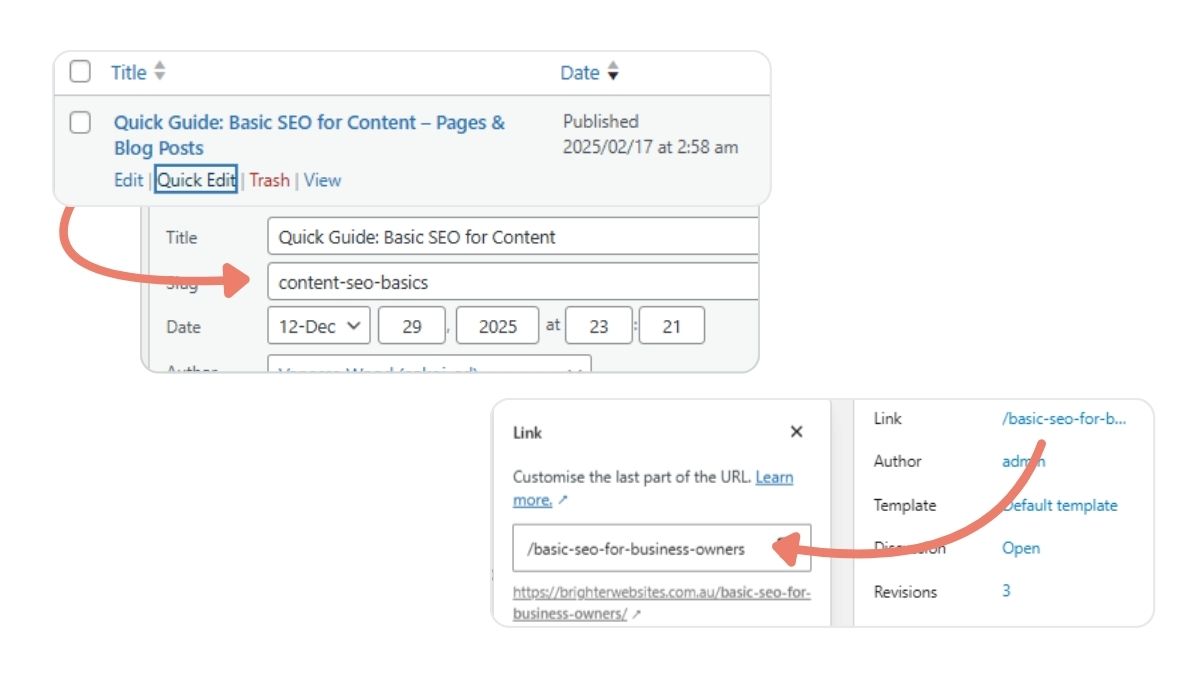
How to Edit in WordPress
- Open the page or post in the default WordPress editor (or click “Quick Edit” from your page list).
- In the right-hand Post settings panel, find the Permalink or URL slug field.
- Type your new slug using natural words, spaces will automatically become hyphens.
(Example: “My New Page” becomes/my-new-page/)
Internal & External Linking
Smart linking is about more than just adding hyperlinks, it’s about building relationships between your content, services, and user intent.
Done right, it improves user flow, strengthens topic authority, and helps both Google and AI systems understand how your pages connect.
Brighter Websites 2026 Linking Philosophy
Every link on your site should have a purpose:
- Internal links guide users deeper into your ecosystem.
- External links prove your authority and credibility.
- CTAs turn intent into measurable action.
When all three work together, your content doesn’t just rank, it converts, informs, and builds authority across both traditional and AI-driven search.
Internal Links
Internal links tell search engines what’s important on your website. When you strategically connect related pages (like service pages, case studies, or guides), you help users, and algorithms, follow a clear pathway through your expertise.
Link to relevant pages within your website to improve user navigation and help Google understand your site structure. If you mention SEO strategies, link to a relevant SEO guide on your website to keep visitors engaged
- Use descriptive anchor text.
- Map services to supporting content.
- Connect your CTAs and internal links intentionally.
External Links
Use external links sparingly and strategically, your goal is to build credibility without leaking traffic. Think of them as citations that validate your claims, not escape routes from your funnel. It’s a signal of transparency and authority, especially in the E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) model.
- Link to reputable, relevant sources.
- Open external links in a new tab to keep users on your site.
- Avoid linking to direct competitors, link to authoritative industry leaders, research, or original data sources instead.
Mobile-Friendliness & Technical Reliability
Technical excellence is no longer just “SEO”; it is a reliability signal. If a site is slow or unstable, AI search engines may discount it as an authoritative source.
- Speed is a Foundation: A Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) under 2.5 seconds is the non-negotiable benchmark for 2026.
- Responsive is Standard: Ensure your site is fully responsive; Google uses mobile-first indexing, meaning your mobile version is the baseline for how AI “reads” your authority.
- Interactive Responsiveness: Aim for an Interaction to Next Paint (INP) score of 200ms or less to ensure the site feels instant to users.
- Test with Search Tools: Use Google PageSpeed Insights or Search Console to monitor Core Web Vitals regularly.
Check Mobile Performance with Googles performance tools or PageSpeed Insights to check speed & fix any issues.
Calls to Action (CTAs) & Engagement Signals
Design your page and content for user conversion, Include relevant CTAs to encourage user interaction (e.g., “Contact us,” “Download our guide,” “Get a free quote”) and Encourage visitors to share, comment, or engage with your content.
Google tracks engagement (clicks, time on page, shares), and higher engagement boosts rankings. Use Google Search Console (GSC) for valuable insights into how your website appears in search results and how users interact with it. You can check Click-Through Rate (CTR), Search Performance, Which Queries & Pages Perform Best and Check Bounce Rate & Dwell Time.
Basics for Technical Search Visibility
Search has evolved beyond keyword and Google and AI systems like ChatGPT and Gemini now interpret meaning and intent. That means your headings and titles should guide both readers and algorithms clearly through your topic.
Best Practices for Titles & Headings
- Use your primary topic or search intent in your H1 (page title) — keep it natural, human, and clear.
- Structure your content logically with H2s, H3s, and H4s that explain key subtopics. This improves accessibility, scanability, and SEO clarity.
- Maintain a consistent hierarchy. If you want a smaller or larger heading visually, change the style, not the HTML level. (Never use heading tags purely for design.)
- Include semantic and related keywords throughout — these help AI systems understand context and build topic authority.
- Avoid keyword stuffing. Read your headings out loud; if they sound robotic, rewrite them conversationally.
Use an AI content optimisation tool like NeuronWriter, Surfer SEO, or MarketMuse to identify semantic gaps and align your content with AI search intent, especially for long-form or location-based service pages.
Writing Optimised Meta Titles & Descriptions
Meta tags aren’t just for human clicks; they are data summaries for AI agents. Check your search preview using tools like Google Search Preview. But Try this: Search for your service and a particular page using a longer question based search, notice the page description and titles may change based on the intent of your search.
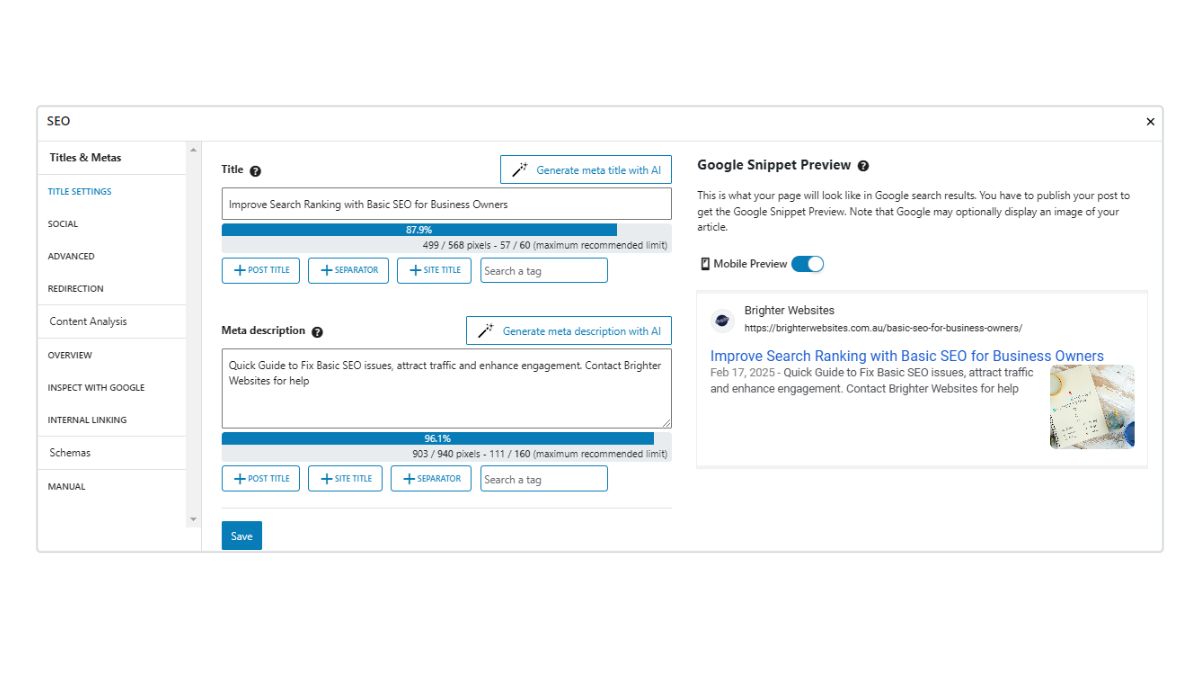
Meta Title Best Practices
- Be Punchy & Direct: Aim for 30–60 characters. While some use the full limit, punchier titles often draw more attention in AI-summarized results.
- Positioning First: Don’t just stuff keywords. Include the concept you want to be known for at the start.
- Entity Clarity: Naturally include your primary service and city/region to help AI anchor your business to a specific location.
Meta Description Best Practices (The “Summary” Shift)
- Summarize, Don’t Advertise: Shift from “marketing teasers” to “concise summaries.” AI uses these descriptions to understand the page’s core purpose instantly.
- The One-Sentence Answer: Write a 140–160 character description that acts as a direct answer to a likely user query.
- Embrace Rewriting: Google now rewrites 60–70% of meta descriptions. Write clearly so if AI pulls text from your page instead, it’s still structured and accurate.
Generate AI-Ready Titles/Metas: Use the SEO Press AI Generate tool to draft your titles, then manually edit them to ensure they lead with your Positioning and the intent behind the page.
Schema (the secret sauce)
Ensure your Schema is active. This is the code that tells AI exactly who you are, what you do, and where you are. It’s the difference between being ‘seen’ and being ‘cited’.
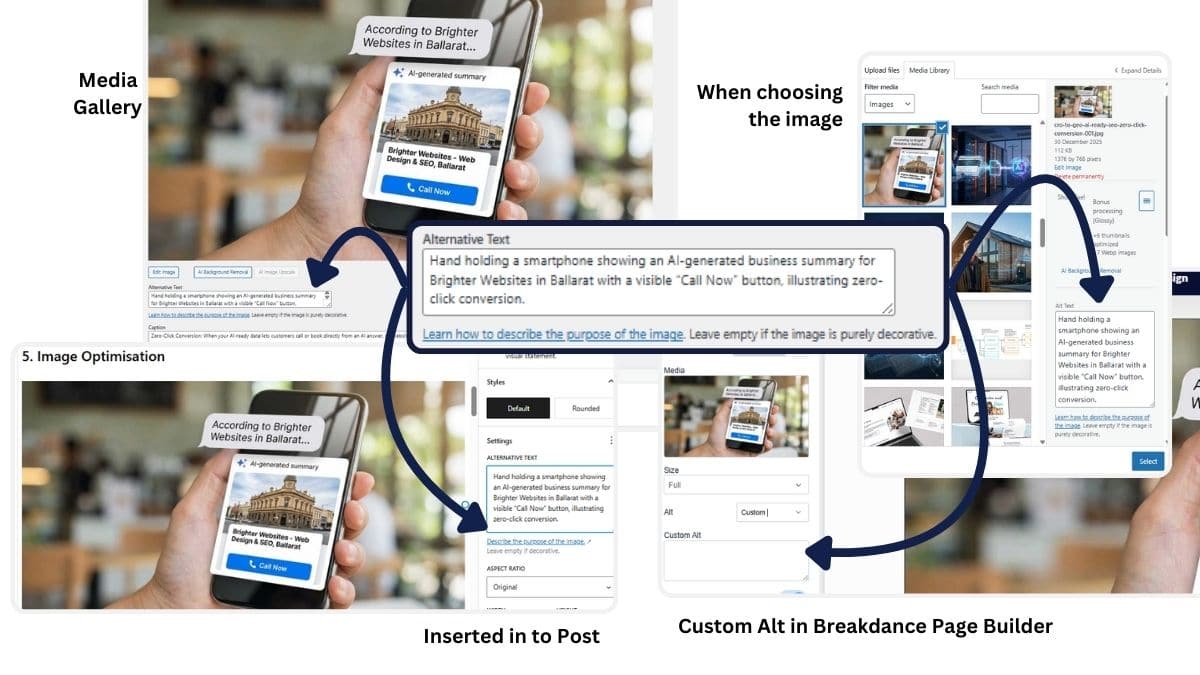
Image Optimisation
Images play a big role in how fast your website loads and how well it ranks in Google. Clean, well-optimised images improve user experience, boost Core Web Vitals, and help search engines (and AI) understand your content better.
Quick Image SEO Checklist
- Rename files before upload, use descriptive, keyword-relevant names (e.g.
ballarat-lawn-care-services.jpginstead ofIMG_0023.jpg). - Add alt text, describe what’s in the image using clear, natural language.
- Compress before upload, use tools like TinyPNG or your site’s optimisation plugin (e.g. LiteSpeed Cache).
- Use WebP format, faster, lighter, and fully supported on modern browsers.
- Add geotags if relevant, local businesses can add simple location data (latitude & longitude) for an extra local SEO signal.
For a full walkthrough on resizing, compressing, and writing effective alt text, see our detailed guide How to Get Image SEO Basics Right at Launch and After Updates
Mastering AI-Ready SEO – Checklist Before Publishing
- The “Known For” Test: Does this page clearly support the one thing you want to be known for? (Positioning > Keywords).
- The Answer-First Test: Is the core value of this page explained in the first 60 words? Is there a direct, concise answer to the user’s main question in the first two paragraphs? (For AI Overviews).
- Proof Markers Added: Have you included a real-world example, a link to a case study, or a “lesson learned”, or “lived experience” detail? (AI ignores generic advice).
- Internal Authority Links: Does this page link to your “Pillar” content to show AI how your topics are clustered?
- Internal Service Pathway: Does this page link to the next logical step in the customer’s journey (e.g., “Book a Strategy Audit”)?
- Heading Hierarchy & Machine-Readable Structure: Are your H2s and H3s framed as questions or clear sub-topics? (No clever/vague titles).
- Meta-Data Summary: Is your Meta Description a factual summary of the page, not a “salesy” teaser?
- Image Alt-Text as Context: Does your Alt-text describe the value of the image, not just a list of keywords?
- Technical Green Lights: Have you checked that the page loads instantly on mobile?
- Clean Infrastructure: Are the URL slugs short and the images compressed for instant mobile loading?
Expert Bonus Tip: The Trust about Automated Tool based SEO Audits & Analysis
Business owners get obsessed with “green lights” in SEO plugins.
- Ahrefs (for advanced insights).
- SEOPress Audit (for a simple SEO check).
- Check Google Search Console
Tools like these are a guide, not a god. A ‘Red Light’ for keyword density or meta description is too long – is fine if the article is brilliant and helpful and the description clearly summarise the intent and purpose of the page.
Don’t ruin your writing just to make a plugin happy. AI values humans, not robots.”
Google Search Console Integration: SEO is not a one-time process, review your content’s performance. Once the page has been live for a week, return to SEOPress. It will pull data from Search Console to show you the actual questions customers are asking to find you. Use these questions to add an FAQ section (Schema-optimized) to the page
See how your page ranks, check if AI is starting to cite you & identify any issues like indexing errors, crawl issues, or keyword gaps.
